Infotainment systems are transforming how we interact with technology, especially in vehicles and homes. From sleek dashboards to smart home hubs, these systems seamlessly blend information and entertainment, offering a personalized and convenient experience. This guide delves into the intricacies of infotainment systems, exploring their evolution, design principles, integration, and the future of this technology.
This overview covers everything from the foundational components of these systems to the latest trends and innovations, providing a complete picture of their impact across various sectors. It also examines the ethical and safety considerations surrounding infotainment systems.
Defining Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems are integrated entertainment and information hubs within vehicles, seamlessly blending communication, navigation, and multimedia capabilities. These systems have evolved significantly from rudimentary audio systems to sophisticated, multi-touchscreen interfaces, profoundly altering the in-car experience. Their impact on driver safety, comfort, and connectivity is undeniable.Modern infotainment systems are not simply about providing entertainment; they are essential components for driver assistance, communication, and even vehicle diagnostics.
Their evolution has been driven by technological advancements and the ever-increasing demand for connected experiences.
Core Functionalities of Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems encompass a wide range of functionalities, significantly impacting the driving experience. These include not only audio and video playback but also communication, navigation, and vehicle diagnostics. This diverse range of functionalities fosters a connected and personalized driving environment.
Evolution of Infotainment Systems
The evolution of infotainment systems reflects the broader advancements in electronics and computing. Early systems primarily focused on audio playback and simple radio tuning. Gradually, features like CD players, satellite navigation, and Bluetooth connectivity were integrated, offering increasing convenience and connectivity. The introduction of touchscreens and advanced processing power ushered in an era of comprehensive infotainment systems, with the capability to manage various aspects of the vehicle and driver experience.
Key Components of Modern Infotainment Systems
Modern infotainment systems are complex assemblages of hardware and software components. These components work in concert to deliver a cohesive and user-friendly experience. Their integration is crucial for seamless operation and optimal user interaction.
Table of Infotainment System Components
| Component Name | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Central Processing Unit (CPU) | Manages all system operations, processing data from various components. | Qualcomm Snapdragon processors in many modern vehicles. |
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) | Handles the rendering and display of graphical information on the screen. | Dedicated GPUs for smooth video playback and interactive maps. |
| Touchscreen Display | Provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with system features. | High-resolution capacitive touchscreens, offering responsive navigation. |
| Audio System | Provides high-quality sound output through speakers. | Premium sound systems with multiple speakers and advanced audio processing. |
| Navigation System | Provides real-time directions and map information. | GPS-based navigation systems offering turn-by-turn directions. |
| Communication Module | Facilitates communication through Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks. | Integrating smartphones for hands-free calling and music streaming. |
| Software Application Suite | Includes various apps for entertainment, communication, and vehicle control. | Pre-installed apps for music streaming, social media access, and vehicle diagnostics. |
Types and Applications of Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems have evolved significantly, seamlessly integrating entertainment and information into various devices. Their applications extend far beyond basic entertainment, impacting user experiences and functionality in vehicles, mobile devices, and even smart homes. This section explores the diverse types and applications of these systems, providing examples and comparisons across different sectors.Infotainment systems are designed to provide a blend of entertainment and information, offering interactive features and functionalities.
This integration is crucial in enhancing user experience and improving the overall functionality of the devices they are embedded in. They often include a variety of media playback options, communication tools, and navigation capabilities.
Automotive Infotainment Systems
Automotive infotainment systems are ubiquitous in modern vehicles. They significantly enhance the driving experience by offering a range of features. The user interface, often displayed on a touchscreen, is designed for intuitive operation while driving. Advanced systems integrate with smartphones, allowing users to access various applications and services directly through the vehicle’s infotainment system.
- Navigation: Advanced mapping capabilities, real-time traffic updates, and destination planning are key features.
- Communication: Bluetooth connectivity, hands-free calling, and smartphone integration enable seamless communication.
- Entertainment: Media playback options, including music streaming services and video streaming, are standard features.
- Vehicle Control: Features such as climate control, seat adjustments, and vehicle settings can be managed through the infotainment system.
Mobile Infotainment Systems
Mobile infotainment systems are increasingly sophisticated, offering a variety of features. These systems integrate seamlessly with smartphones, providing a central hub for communication, entertainment, and information access.
- Entertainment: Mobile devices often feature multimedia playback options, games, and access to streaming services, providing a wide range of entertainment choices.
- Navigation: GPS-based navigation, maps, and real-time traffic updates are common features, enabling users to navigate efficiently.
- Communication: Features such as messaging, email, and social media integration provide a platform for communication and information sharing.
- Productivity: Task management tools, calendars, and note-taking apps are commonly integrated into mobile infotainment systems.
Home Infotainment Systems
Home infotainment systems are increasingly integrated into smart home ecosystems, automating tasks and enhancing the user experience. They provide a central platform for controlling various aspects of the home, including lighting, temperature, security, and entertainment.
- Automation: Home infotainment systems allow users to control various devices in the home through a centralized interface. This automation can be programmed for specific times or triggered by user input, increasing convenience.
- Entertainment: These systems often include integrated media players, streaming services, and high-quality audio systems, creating a home entertainment hub.
- Security: Some systems integrate with home security systems, enabling remote monitoring and control.
- Energy Management: Integration with smart appliances allows for optimized energy consumption.
Comparison of Automotive Infotainment Systems
Different vehicle manufacturers offer varying levels of infotainment system sophistication. High-end vehicles often feature advanced features such as voice recognition, gesture control, and augmented reality navigation. Lower-priced vehicles might offer a more basic system, focusing on essential features such as audio playback and basic navigation.
| Feature | High-End System | Basic System |
|---|---|---|
| Navigation | Advanced mapping, real-time traffic, augmented reality | Basic maps, offline routing |
| Voice Recognition | Comprehensive voice commands for various functions | Limited voice commands for basic functions |
| Touchscreen Size and Resolution | Large, high-resolution touchscreen | Smaller, lower-resolution touchscreen |
| Connectivity | Integration with multiple apps and services | Limited connectivity options |
User Interface Design and Experience
Infotainment systems are increasingly sophisticated, demanding intuitive and engaging user interfaces. A well-designed user interface (UI) significantly impacts user satisfaction and adoption of these systems. The user experience (UX) is crucial for seamless integration of infotainment features into the overall driving experience. Properly designed systems are crucial to reducing driver distraction and maximizing usability.
Key Design Principles for Intuitive Interfaces, Infotainment systems
Effective infotainment UI design prioritizes simplicity and clarity. Users should be able to readily understand and navigate the system’s functions without extensive training. Consistent design elements, such as button placement and visual cues, enhance predictability and usability. Clear visual hierarchies guide users through information and tasks, and well-defined feedback mechanisms inform users about the system’s responses. These principles aim to minimize cognitive load on the driver, improving overall safety and satisfaction.
Different User Interaction Methods
Various interaction methods shape the infotainment experience. Touchscreens provide a visual and tactile interface for selecting options and controlling functions. Voice control allows hands-free operation, facilitating safety-conscious interactions. Haptic feedback, such as subtle vibrations, provides confirmation and enhances the overall user experience. These diverse methods cater to individual preferences and driving situations, while maintaining usability and safety.
UI Design Patterns and User Experience
Different UI design patterns contribute to varied user experiences. A well-structured table showcases the correlation:
| UI Design Pattern | Associated User Experience Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Tabbed Interface | Provides organized access to different functionalities. Clear visual separation enhances user understanding. |
| Carousel Interface | Dynamically presents information. Easy to scan and discover new content, but potential for information overload. |
| Tile-Based Interface | Visually appealing, intuitive for browsing and selecting options. Large icons allow quick recognition and interaction. |
| Hierarchical Menus | Structure content logically, enabling users to navigate through multiple levels of options. Complex systems might require a more structured approach. |
| Contextual Menus | Displays relevant options based on the current context. Reduces clutter and improves efficiency for specific tasks. |
Accessibility in Infotainment Design
Ensuring accessibility for diverse user groups is paramount. Features like adjustable font sizes, color contrast options, and alternative input methods (like voice commands or physical buttons) are crucial for inclusivity. Considering users with disabilities or visual impairments is essential for a truly user-friendly infotainment system. Clear and accessible information for users with varying levels of technical proficiency ensures a smooth experience for everyone.
Integration with External Services
Infotainment systems are increasingly reliant on seamless integration with external services to provide a rich and dynamic user experience. This integration allows for access to real-time data, personalized content, and enhanced functionalities. The methods employed for these integrations are crucial to the system’s overall performance and user satisfaction.Connecting infotainment systems with external services involves a complex interplay of protocols, security measures, and technical architecture.
Proper integration ensures that the system functions reliably and securely, while maintaining a positive user experience.
Methods and Protocols for Integration
External service integration often utilizes Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). APIs define the methods and data formats that applications can use to communicate with each other. RESTful APIs are a common choice for their simplicity and scalability. Other protocols like SOAP can also be employed, though RESTful APIs are generally preferred for their efficiency. Specific protocols used will depend on the service provider’s API specifications.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount when integrating infotainment systems with external services. Sensitive user data, such as location information or payment details, may be exchanged. Robust security measures, including encryption and authentication protocols, are essential to protect this data. Implementing secure communication channels using HTTPS and employing strong encryption algorithms is critical to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Multi-factor authentication can add another layer of security, protecting against unauthorized access attempts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Integrating with Specific External Services
Integrating with navigation apps, such as Google Maps or Waze, offers real-time traffic updates and alternative route suggestions, enhancing the driving experience. However, reliance on external services may introduce latency issues, particularly during periods of high network congestion. Similarly, integrating music streaming services provides personalized music selections, but it might require a subscription or usage-based fees. Data usage can increase, which impacts the battery life of the device.
Technical Architecture for Cloud-Based Connections
The technical architecture behind connecting infotainment systems with cloud-based services typically involves several key components. Firstly, an application layer handles the interaction with external APIs, ensuring seamless communication. Secondly, a middleware layer acts as a bridge between the infotainment system and the cloud services, managing authentication and data exchange. Finally, a database layer stores the necessary data, such as user preferences and service credentials, in a secure manner.
Data Management and Privacy
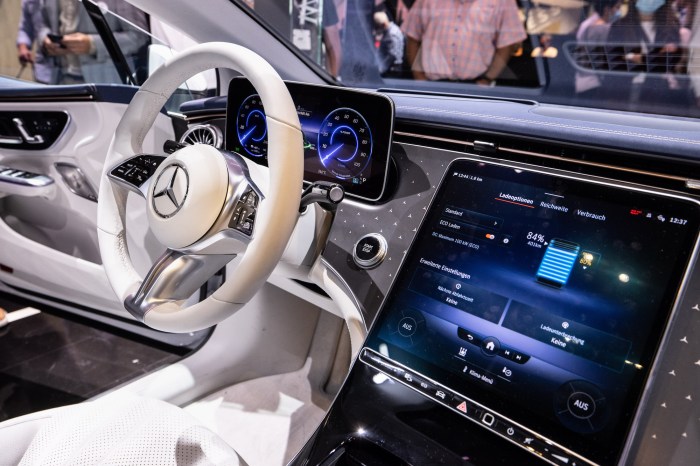

Infotainment systems collect and process vast amounts of user data, from driving habits and preferences to location and interaction with in-car applications. Understanding how this data is handled, secured, and the privacy implications is paramount for building trust and responsible systems. This section delves into the data lifecycle within infotainment systems, security measures, the importance of user consent, and relevant regulatory frameworks.
Data Collection, Processing, and Storage
Infotainment systems collect diverse data points through various means, including sensors, GPS, user interactions with apps, and vehicle diagnostics. This data is often processed to enhance user experience, personalize features, and provide valuable insights for the automotive manufacturer. The collected data is stored on the vehicle’s onboard system, and often, also on remote servers for backup and processing.
Data storage protocols are implemented to comply with data retention policies. This ensures that user data is kept securely and according to legal and ethical standards.
Security Measures for User Data Protection
Robust security measures are crucial to protect sensitive user data. These measures include encryption of data both in transit and at rest, access controls to limit unauthorized access, and regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities. Multi-factor authentication and secure communication protocols are implemented to prevent unauthorized access. Examples of such protocols include TLS (Transport Layer Security) and similar encryption standards.
Data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques can be applied to reduce the risk of re-identification and maintain user privacy.
Importance of Data Privacy and User Consent
Data privacy is a fundamental aspect of infotainment systems. Transparency regarding data collection practices and user rights is vital. Users should be clearly informed about the types of data collected, how it will be used, and the potential implications for their privacy. User consent is essential, enabling users to control the collection and use of their data.
Obtaining explicit consent for data collection and usage is a critical part of maintaining trust and upholding ethical standards. For instance, users should be presented with clear options for data sharing, and they must have the ability to opt out or modify their consent.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Data Privacy
Various regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), govern data privacy. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for infotainment systems operating in regions where these laws apply. These regulations often require companies to be transparent about their data practices, provide users with control over their data, and be accountable for data breaches.
These regulations aim to balance the need for innovation in infotainment systems with the protection of user privacy rights. Adherence to these frameworks is essential to avoid legal ramifications.
Future Trends and Innovations
Infotainment systems are constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and user expectations. Emerging trends like artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and enhanced connectivity are reshaping the landscape, promising a future of more intuitive, personalized, and engaging experiences. This evolution necessitates a deep understanding of the technological shifts and their potential impact.The future of infotainment systems is marked by a convergence of technologies, each contributing to a more seamless and enriching user experience.
AI-powered personalization, for example, is already making strides in customizing content delivery and service recommendations. The increasing availability of high-bandwidth connectivity is laying the groundwork for immersive experiences, such as those enabled by AR and VR.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is fundamentally altering infotainment systems. AI-driven algorithms analyze user preferences, driving personalized content recommendations and adjusting system settings to optimize user experience. For instance, AI can predict a user’s preferred music genre based on their past listening habits and proactively suggest new artists or playlists. Machine learning allows systems to adapt and improve their functionality over time, refining their performance and efficiency.
This ongoing learning enhances the effectiveness of features like voice assistants and navigation systems.
Augmented and Virtual Reality Integration
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are transforming the way users interact with infotainment systems. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing existing experiences. For example, AR navigation overlays real-time directions onto the driver’s view of the road, providing clear guidance and minimizing distractions. VR, on the other hand, creates immersive virtual environments. In infotainment, VR can be used to simulate realistic driving scenarios or to create interactive gaming experiences, offering users a more engaging and immersive experience.
Potential Future Features
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Personalized News Feeds | Tailored news content based on user interests, providing a more relevant and engaging news experience. |
| Predictive Maintenance for Vehicle Systems | Proactive identification of potential vehicle issues, enabling preventative maintenance and reducing unexpected breakdowns. |
| AI-Powered Interactive Storytelling | Dynamic narratives and character development, creating more engaging and personalized entertainment experiences. |
| Interactive 3D Maps with Augmented Reality Navigation | Detailed 3D representations of locations, augmented with real-time directions and interactive elements, enhancing navigation and exploration. |
| Personalized in-car shopping and entertainment experiences | Tailored product recommendations, movie suggestions, and other content based on user preferences and location. |
Technical Specifications and Performance
Infotainment systems are increasingly sophisticated, demanding robust technical underpinnings to deliver a seamless and engaging user experience. This section delves into the key technical specifications and performance metrics that define high-performing systems. From the hardware components to the display technologies and performance benchmarks, a comprehensive understanding of these elements is critical for developers and consumers alike.
Infotainment systems are a must-have these days, offering a range of features. However, customizing your vehicle’s appearance, like installing lowering kits, can significantly affect the overall aesthetic and handling experience. Choosing the right lowering kits can greatly enhance the car’s look, which, in turn, can boost your enjoyment of the car’s infotainment system and overall driving experience.
Hardware Components
The efficient operation of an infotainment system relies heavily on the integrated hardware. A robust system architecture is essential to support complex functionalities like navigation, entertainment, and communication. Key hardware components include:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU’s processing power dictates the system’s responsiveness and ability to handle multiple tasks concurrently. Higher clock speeds and more cores lead to smoother transitions between applications and a quicker response to user input.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The GPU is crucial for rendering high-quality graphics, especially in displays featuring 3D maps, animated menus, and visually rich interfaces. A powerful GPU ensures smooth animations and realistic visualizations.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM plays a pivotal role in multitasking. Sufficient RAM allows the system to handle numerous applications and data streams simultaneously without performance degradation. More RAM generally translates to a more responsive system.
- Storage: Internal storage space dictates the amount of data the system can store, from music libraries and apps to downloaded maps and user settings. Larger storage capacity allows for more content and a wider range of applications.
- Connectivity Modules: These include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular connectivity. High-performance modules ensure seamless and fast communication with external devices and services.
Display Technologies
The display technology significantly impacts the user experience. Various technologies offer different advantages in terms of resolution, clarity, and power consumption.
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display): LCDs are prevalent due to their affordability and relatively low power consumption. However, they may not match the brightness and color accuracy of other technologies.
- OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode): OLEDs offer superior color accuracy, higher contrast ratios, and deeper blacks, leading to a more immersive visual experience. However, they often come with a higher price tag compared to LCDs.
- AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode): A sub-category of OLEDs, AMOLEDs exhibit enhanced color reproduction and brightness, contributing to vivid and sharp visuals. They are known for their energy efficiency, making them ideal for infotainment systems.
Performance Benchmarks
Evaluating infotainment systems necessitates standardized benchmarks. These metrics assess the system’s responsiveness, stability, and overall performance under various conditions.
- Response Time: This measures the time taken for the system to respond to user input, such as button presses or touchscreen interactions. Faster response times lead to a more intuitive and user-friendly experience.
- Frame Rate: This refers to the number of frames displayed per second. Higher frame rates result in smoother animations and transitions, enhancing visual appeal and user experience.
- CPU Utilization: This metric indicates the percentage of the CPU’s processing power consumed by different tasks. Low CPU utilization ensures that the system remains responsive even under heavy loads.
- Power Consumption: Energy efficiency is crucial for portable infotainment systems. Lower power consumption contributes to longer battery life and reduces the environmental impact.
Cost and Economic Factors
Infotainment systems are increasingly sophisticated and integral to the modern automotive experience. Understanding the cost implications of development, deployment, and integration is crucial for both manufacturers and consumers. This analysis delves into the financial aspects of infotainment systems, encompassing the costs of various technologies, their impact on vehicle pricing, and how pricing affects market demand.
Cost Factors in Infotainment System Development
Several key factors contribute to the cost of developing and implementing infotainment systems. Hardware costs, encompassing the processors, displays, and other components, can vary significantly depending on the desired features and performance levels. Software development, encompassing the operating system, applications, and user interface design, is another substantial cost element. Integration with external services, such as navigation apps or music streaming platforms, also incurs costs related to licensing fees and data transfer.
Labor costs for engineers, designers, and testers also contribute to the overall expenditure.
Comparison of Infotainment System Technologies
Different technologies offer varying levels of functionality and performance, leading to differing cost structures. For example, systems based on advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) often have higher development and implementation costs compared to systems with more basic functionalities. Systems employing cloud-based services may also have higher ongoing costs due to data transfer and storage fees. Furthermore, the choice between in-house development and outsourcing of certain components will significantly affect the overall cost.
The decision regarding the level of integration and complexity in the user interface also impacts the costs associated with development.
Impact on Vehicle Pricing
The inclusion of infotainment systems influences vehicle pricing significantly. The cost of developing and implementing these systems is often passed on to the consumer through higher vehicle prices. The more sophisticated the system, the greater the impact on the final price. For instance, a premium vehicle with advanced features like augmented reality navigation and personalized in-car experiences will likely have a higher price point than a basic model with standard connectivity features.
Furthermore, the ongoing costs of maintaining and updating the software, as well as the potential for future feature enhancements, can also contribute to the price.
Impact on Market Demand
The price of infotainment systems affects market demand. Consumers are often willing to pay a premium for advanced features and sophisticated user experiences. However, high prices can also limit the market reach, especially in price-sensitive segments. Market research indicates that a balance between features and affordability is crucial for maximizing demand. Manufacturers need to carefully consider the trade-off between cost and functionality to attract a broader customer base.
An effective strategy involves offering various tiers of infotainment systems, each catering to different price points and customer needs.
Impact on Driving Safety

Infotainment systems, while offering a multitude of features, present both opportunities and challenges concerning driver safety. The integration of entertainment, communication, and navigation functionalities can significantly influence a driver’s focus and reaction time. Careful design is crucial to mitigate risks and leverage the potential benefits for a safer driving experience.Infotainment systems’ potential to enhance driving safety is substantial.
They can facilitate tasks like navigation and communication, potentially reducing driver workload and errors. However, the very nature of these systems introduces distractions, posing risks if not implemented and designed prudently. A key focus is on minimizing these distractions to promote driver safety.
Potential Risks of Infotainment Systems
Infotainment systems, while offering many convenient features, can distract drivers. This distraction can stem from various sources, such as complex menus, notifications, and interactive features. The cognitive load associated with navigating these systems can divert attention from the road, potentially leading to accidents. Furthermore, visual displays and auditory alerts can also compete with important visual and auditory cues from the driving environment, thereby impacting driver awareness.
Potential Benefits of Infotainment Systems
These systems can enhance safety through various features. Navigation systems, for example, can provide real-time traffic updates, minimizing travel time and reducing the risk of getting lost. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) integrated into infotainment platforms can alert drivers to potential hazards, potentially reducing accidents. These systems also allow for hands-free communication, thus potentially preventing distracted driving.
Infotainment systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering drivers a wealth of features. They’re moving beyond basic navigation and entertainment to encompass a wider range of functions, and this is particularly relevant in the context of sustainable mobility. These systems can, for instance, optimize routes to minimize fuel consumption, provide real-time data on charging stations, and even suggest eco-driving techniques.
Ultimately, infotainment systems are playing a key role in shaping the future of driving.
Designing Safe Infotainment Systems
Designing infotainment systems that minimize distractions is crucial for enhanced driver safety. User interfaces (UIs) should be intuitive and easy to navigate. Complex menus and unnecessarily intricate designs should be avoided. Furthermore, information should be presented in a clear and concise manner, minimizing the cognitive load on the driver. A crucial factor is limiting the need for manual input while driving.
Minimizing Distractions
Distraction-minimizing strategies are vital for safe infotainment design. Voice commands are one effective solution, allowing drivers to control features without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road. Furthermore, visual displays should be strategically placed and designed to be easily seen without requiring constant eye movement away from the road. Important alerts should be visually prominent and clearly differentiated from other information.
Human-Machine Interaction
The design of infotainment systems must account for the human factor. Understanding how drivers interact with technology and their cognitive limitations is crucial. A safe infotainment system will consider the driver’s needs and limitations in their design. It should allow for a natural, intuitive, and effortless interaction with the system, reducing the risk of mistakes and errors.
By considering these factors, designers can create systems that improve driver awareness and reduce the chance of accidents.
Examples of Safe Infotainment Features
One example is a navigation system that provides clear, concise turn-by-turn directions, reducing the need for constant visual input from the system. Another example is a hands-free communication system that allows for clear voice commands, minimizing manual inputs and cognitive load. Integration of advanced driver-assistance systems, which use sensors to detect potential hazards, can be another useful safety feature, prompting alerts in a clear and concise way.
Ethical Considerations
Infotainment systems, while enhancing the driving experience, introduce novel ethical considerations. Their features and data collection practices necessitate careful examination to ensure responsible deployment and mitigate potential harm. The increasing integration of these systems into vehicles raises questions about user autonomy, data privacy, and the potential for manipulation.Modern infotainment systems are not mere entertainment devices; they are increasingly sophisticated tools that influence user behavior and decision-making.
The design and functionality of these systems can inadvertently shape how drivers interact with their surroundings and make choices behind the wheel. Understanding these subtle influences is crucial for responsible development and implementation.
Ethical Implications of Infotainment Features
Infotainment systems’ features can sometimes lead to ethical dilemmas. For example, personalized recommendations for music, navigation, or entertainment options might unintentionally promote certain preferences over others. This subtle form of algorithmic bias can inadvertently reinforce existing societal norms or prejudices. Furthermore, advanced features like voice assistants or augmented reality overlays can potentially distract drivers, posing a risk to safety and raising ethical concerns about the system’s ability to prioritize user well-being.
Role of Infotainment Systems in Influencing User Behavior
Infotainment systems exert influence on user behavior through various mechanisms. Interactive features and personalized recommendations subtly guide user choices, potentially shaping preferences and habits. For instance, frequent use of navigation apps might alter drivers’ understanding of spatial awareness, potentially leading to over-reliance on the system rather than developing a personal sense of route knowledge. Furthermore, features that reward certain behaviors or encourage engagement can lead to undesirable outcomes, such as prioritizing entertainment over essential driving tasks.
Examples of Ethical Concerns Raised by Infotainment Systems
Several examples illustrate how infotainment systems can raise ethical concerns. The potential for targeted advertising within the infotainment system raises privacy concerns, especially if user data is not adequately protected or used transparently. Another concern is the manipulation of user preferences through tailored recommendations, which could potentially create a filter bubble or limit exposure to diverse perspectives. The use of facial recognition for driver identification, while potentially improving safety, raises concerns about data security and potential misuse of the technology.
Ethical Considerations in Data Collection
The data collected by infotainment systems raises critical ethical considerations regarding privacy and security. The vast amount of data gathered, encompassing user preferences, location history, and interaction patterns, necessitates strong data protection measures. Transparency in data collection practices and user consent are essential to ensure user autonomy and trust. Furthermore, the potential for data breaches and misuse of sensitive information requires robust security measures to safeguard user privacy.
Clear guidelines on data retention, usage, and sharing are necessary to mitigate these risks. For instance, the storage of user driving habits and location history should be subject to strict privacy protocols and adhere to regulations like GDPR. The collection of such data must be clearly justified and directly linked to the intended functionality of the infotainment system.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, infotainment systems have become an integral part of modern life, enriching our experiences and shaping the future of technology. From user interface design to data management and ethical considerations, this exploration highlights the multifaceted nature of these systems. Their continued evolution promises even more sophisticated and integrated experiences in the years to come.
FAQ Insights: Infotainment Systems
What are the key components of a typical infotainment system?
Key components include a central processing unit (CPU), display screen, input devices (touchscreen, voice controls), and communication modules for connecting to external services. The specific components vary depending on the type and application of the infotainment system.
How do infotainment systems impact driving safety?
While infotainment systems can enhance safety through features like navigation and hands-free calling, they also pose risks if not used responsibly. Proper design, minimizing distractions, and clear user interfaces are crucial for enhancing safety while using these systems.
What are the security concerns associated with infotainment systems?
Infotainment systems often collect and process user data, making them vulnerable to security breaches. Strong encryption, secure authentication protocols, and regular software updates are essential for safeguarding user data and preventing unauthorized access.
How do infotainment systems use user data?
Infotainment systems gather data on user preferences, usage patterns, and location to personalize the user experience and provide relevant information. Proper data handling and user consent are crucial to address privacy concerns.